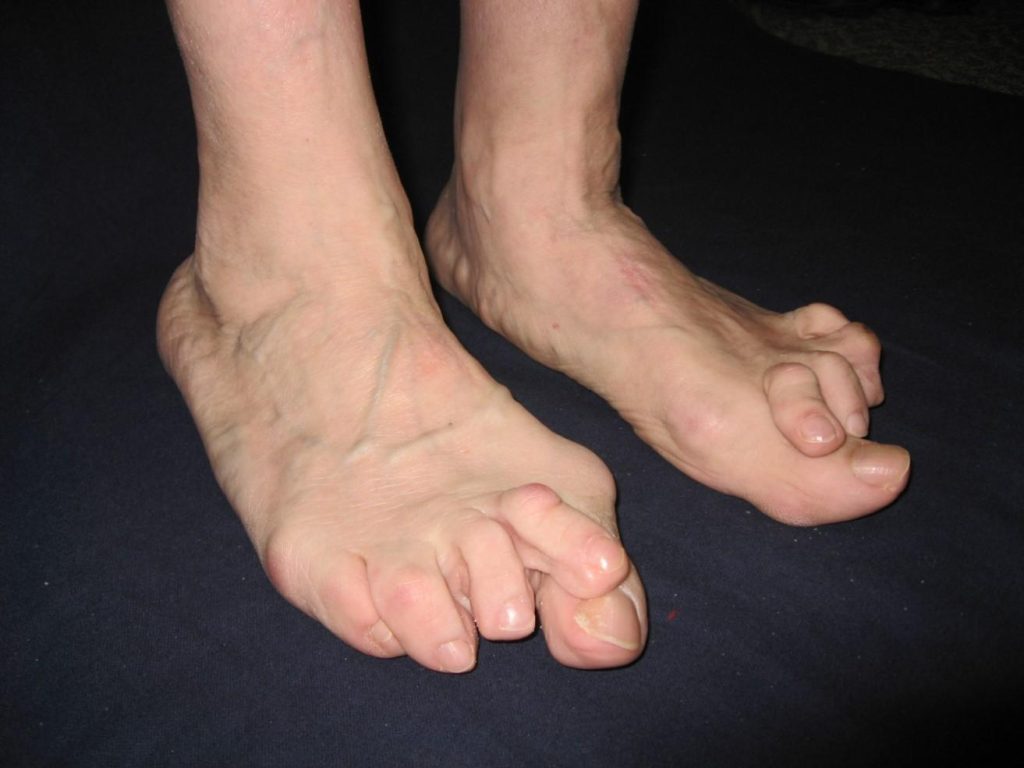
Rheumatic foot deformity refers to structural changes in the foot caused by rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a chronic autoimmune condition that leads to joint inflammation, damage, and deformity.
Common Deformities:
- Forefoot:
- Hallux valgus (bunion)
- Claw toes or hammer toes
- Subluxation or dislocation of metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints
- Midfoot:
- Collapse of the arch (pes planus or flatfoot)
- Hindfoot:
- Valgus deformity (heel tilts outward)
- Tibiotalar and subtalar joint arthritis
Causes:
- Chronic synovitis and joint erosion
- Ligament and tendon weakening
- Mechanical imbalance over time
Symptoms:
- Pain, swelling, and stiffness
- Joint deformity and instability
- Difficulty walking and fitting shoes
- Calluses and ulcers in severe cases
Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination
- Blood tests (e.g., rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP)
- X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI to assess joint damage
Treatment:
- Medical: Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, NSAIDs
- Orthotic: Special footwear, insoles, braces
- Surgical: Joint fusion, tendon reconstruction, or deformity correction in advanced cases
