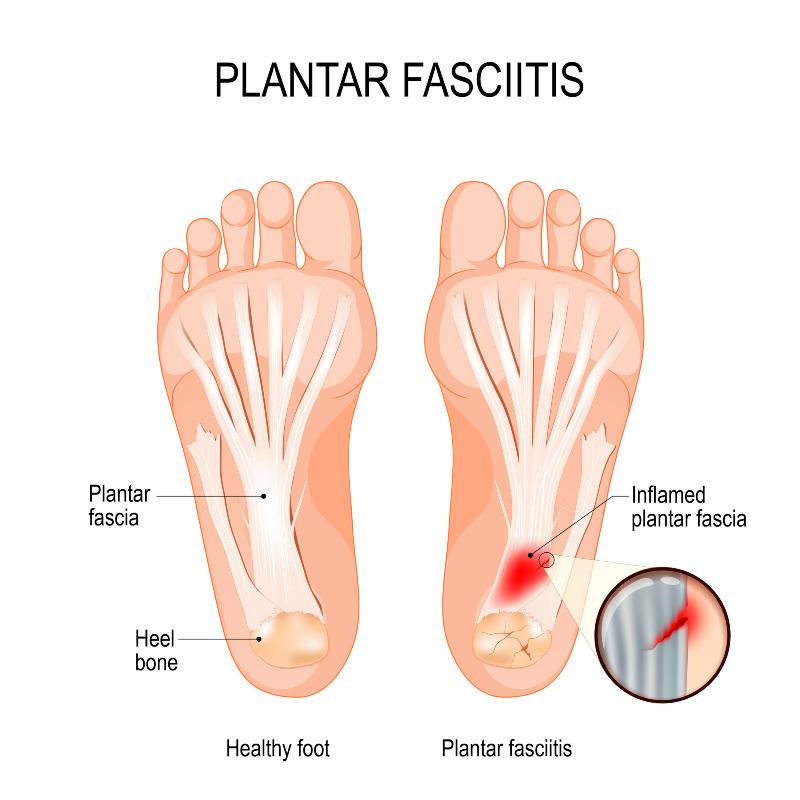
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
- Definition: Explain that plantar fasciitis involves inflammation or degeneration of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue connecting the heel bone to the toes .
- Anatomy: Include diagrams illustrating the plantar fascia’s location and function in supporting the foot’s arch.
- Causes: Discuss contributing factors such as overuse, foot structure abnormalities (e.g., flat feet or high arches), improper footwear, and sudden increases in physical activity
Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Common Symptoms:
- Sharp or stabbing heel pain, especially with the first steps in the morning or after prolonged rest .
- Pain that decreases with activity but may return after extended periods of standing or walking.
- Diagnostic Process:
- Physical examination focusing on tenderness in the heel area.
- Assessment of foot mechanics and gait.
- Imaging tests (e.g., X-rays or MRIs) if necessary to rule out other conditions
Risk Factors
- Intrinsic Factors:
- Age (commonly affects individuals between 40–60 years) .
- Foot mechanics, such as flat feet or high arches.
- Tight calf muscles or Achilles tendons.
- Extrinsic Factors:
- Occupations requiring prolonged standing or walking on hard surfaces.
- Wearing unsupportive footwear.
- Obesity, which increases stress on the plantar fascia
Treatment Options
- Conservative Treatments:
- Rest and activity modification.
- Stretching exercises targeting the plantar fascia and calf muscles .
- Use of ice packs to reduce inflammation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen .
- Supportive Measures:
- Orthotic devices to support the arch.
- Night splints to maintain foot dorsiflexion during sleep .
- Advanced Therapies:
- Physical therapy focusing on strengthening and flexibility.
- Corticosteroid injections for persistent cases.
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) as a non-invasive option .
- Surgical Intervention:
- Considered when conservative treatments fail after 6–12 months.
- Procedures may involve partial release of the plantar fascia
Consult your Planter fasciitis specialist in Ahmedabad for better outcome.
